Hydraulic Piston Pumps Versus Hydraulic Gear Pumps

The type of hydraulic pump you need depends on a variety of factors, including, but not limited to, the type of hydraulic fluid used in your machinery, operating pressure, application speed, and flow rate requirements.
Two of the most common pumps used in hydraulic equipment are piston pumps and gear pumps. This article will highlight everything you need to know about each pump, including its common uses and benefits.
Hydraulic Piston Pump

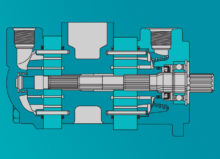
A piston pump is a positive displacement pump that uses reciprocating motion to create rotation along an axis. Some piston pumps have variable displacement, while others have a fixed displacement design.
Advantages & Uses
A hydraulic piston pump is capable of the highest pressure ratings and is commonly used to power heavy-duty lifts, presses, shovels, and other components.
Piston-style pumps also have complex internal components that often allow them to vary the displacement per revolution.
The downside of piston pumps is that they are often more expensive (especially when compared to gear pumps). Still, their improved efficiency often makes them a better investment for long-term production.
Hydraulic Gear Pumps
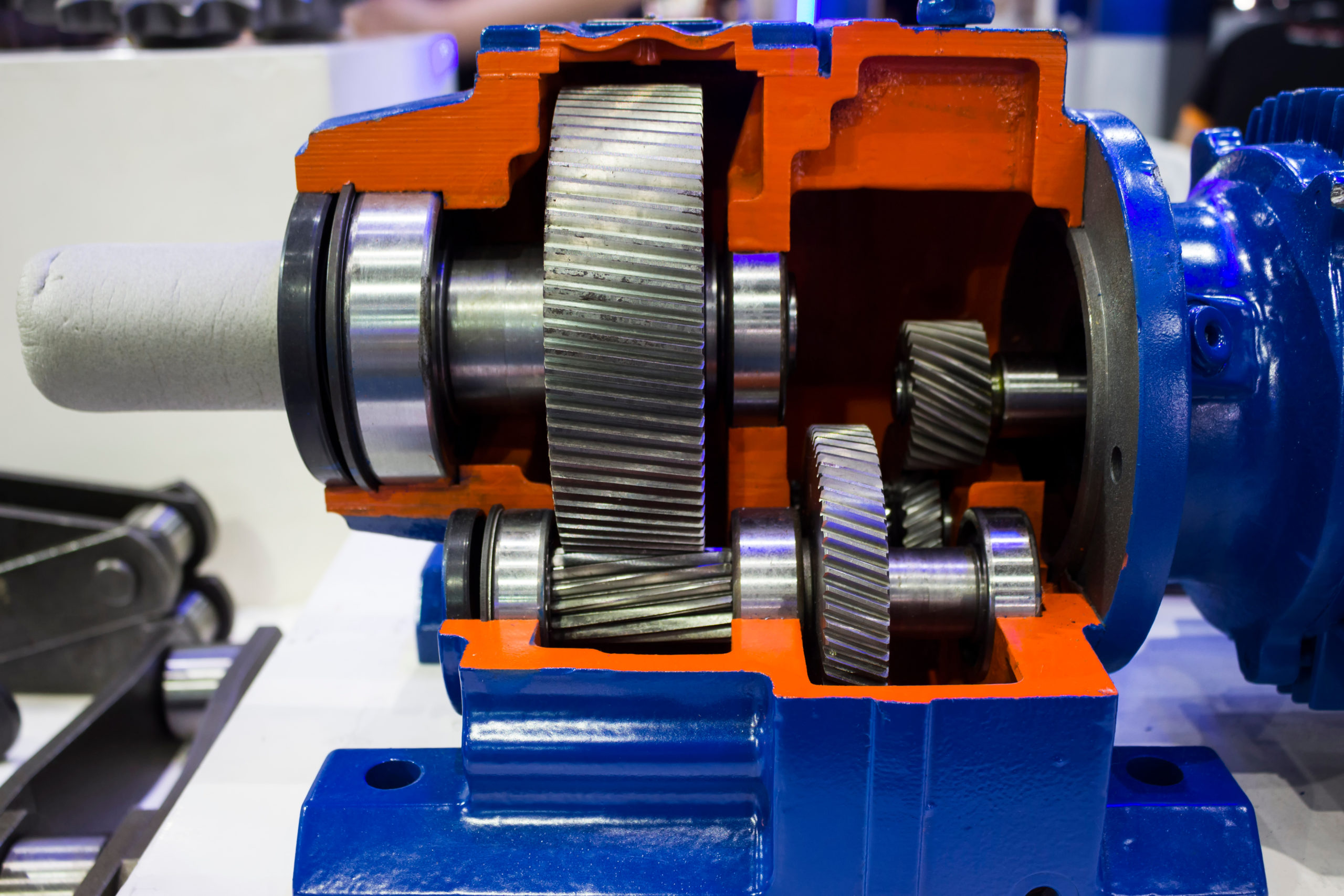

Gear pumps use gears or cogs to transfer fluids. The cogs are tightly aligned to create suction as they draw liquid in and discharge it. The gears can be internal or external, depending on the application. Gear pumps are also positive displacement pumps, but they are always fixed displacement, so you would need separate pumps or valves to control the amount of displacement.
Advantages & Uses
Gear pumps are known for being reliable and durable when they are well-maintained. Compared to piston pumps, they also don’t require as much maintenance and are typically more affordable. However, these pumps usually max out at 3000 PSI. While this is enough pressure to power some machinery, it may not have the power to operate large presses and other industrial equipment. A gear-style pump also lacks the ability to vary the displacement of your system.
Gear pumps are often used in low-pressure applications where dispensing high-viscosity liquids is required. They are typically used in the food and beverage, pulp and paper, and oil/chemical industries.
Key Differences Between Hydraulic Piston Pumps & Gear Pumps
The primary difference between a gear pump and a piston pump is how they are designed. While both pumps need hydraulic fluid to generate mechanical power, a piston pump uses a piston to move liquid throughout the pump valves, while a gear pump uses cogs to move fluid throughout the pump.
Do You Need a Piston Pump or a Gear Pump?
As previously mentioned, your application requirements will largely determine what type of pump you need.
Gear pumps are affordable for low-pressure applications (35 to 200 bar or 507 to 2900 PSI), while piston pumps are more efficient options for high-pressure applications. A piston pump is also a better option if you’re looking for a pump with a higher discharge rate. Lastly, a piston pump will provide the most efficiency if your application is high-speed.
Purchase Replacement Pumps From Panagon Systems
Founded over 25 years ago. Panagon Systems specializes in manufacturing cost-efficient obsolete or discontinued piston pumps, motors, and replacement components from brands like Vickers/Eaton, Caterpillar, and Rexroth. All pumps we manufacture are made in-house in the United States and are guaranteed to meet OEM specifications.
If you’re looking for cost-effective and timely pump replacement options, you’re looking for us. Contact us today for help in selecting the right pump for your application, or to request a product quote.